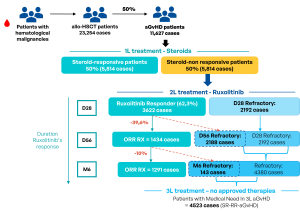
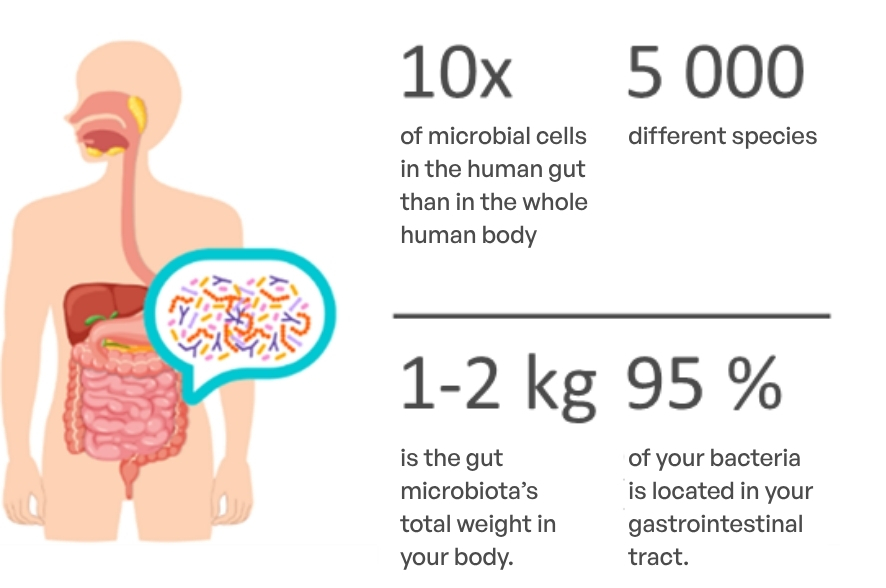
Graft-versus-Host Disease (GvHD) is a serious complication that can occur after an allogeneic stem cell transplant, a common treatment for blood cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma. GvHD happens when the donated hematopoietic stem cells view the recipient’s body as foreign and start attacking healthy tissues and organs.
There are two main forms of GvHD: acute GvHD (aGvHD), that occurs within the first 100 days post-transplant, and chronic GvHD (cGvHD), that develops after 100 days or more. Both types can significantly impact survival rates and quality of life after stem cell transplantation. The symptoms of each form also vary significantly.